Will A Posterior Calcaneal Spur Cause Pain?
Overview
Heel spurs occur in at least half the people who have plantar fasciitis, a painful condition involving the thick tissue that runs between your heel bone and your toes. In the past, doctors often performed surgery to remove heel spurs, believing them to be the cause of the pain associated with plantar fasciitis. In treating plantar fasciitis now, doctors rely more on ice, arch supports, physical therapy and pain medications, and surgery is rarely performed.
Causes
Heel spurs develop in some people that have a condition called plantar fasciitis, inflammation of the plantar fascia. Heel spurs form when the plantar fascia separates from the calcaneus. An abnormal bone growth, a hook-like spur, forms from calcium deposits that grow at the site of inflammation. Heel spurs are more common in middle-aged adults and people that have had plantar fasciitis for a long time. People with flat feet or high arches are vulnerable to heel spurs. Women who wear high-heeled shoes are more susceptible, as well.
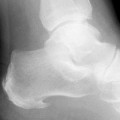
Symptoms
The vast majority of people who have heel spurs feel the asscociated pain during their first steps in the morning. The pain is quite intense and felt either the bottom or front of the heel bone. Typically, the sharp pain diminishes after being up for a while but continues as a dull ache. The pain characteristically returns when first standing up after sitting for long periods.
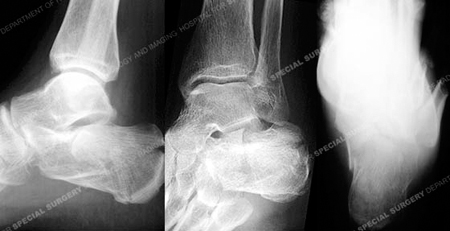
Diagnosis
Heel spurs and plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your heel spur or plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to heel spurs and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays will show calcification or bone within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus. This is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of Heel Spurs is the same as treatment of plantar fasciitis. To arrive at an accurate diagnosis, our foot and ankle Chartered Physiotherapists will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the physio will rule out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. The following treatment may be used. Orthotics/Insoles. Inflammation reduction. Mobilisation. Taping and Strapping. Rest.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to correct for heel spur syndrome is a common procedure which releases plantar fascia partially from its attachment to the calcaneous (heel bone). This part of the surgery is called a plantar fasciotomy due to the fact the fascia is cut. This is most often done through an open procedure as any heel spur or bursa can be removed at the same time. If the spur is not removed during the surgery, it will probably be just as successful, as the large spur is not the true problem. Some physicians use an endoscopic approach (EPF) where a small camera aids the physician during surgery with typically smaller incisions on each side of your foot.